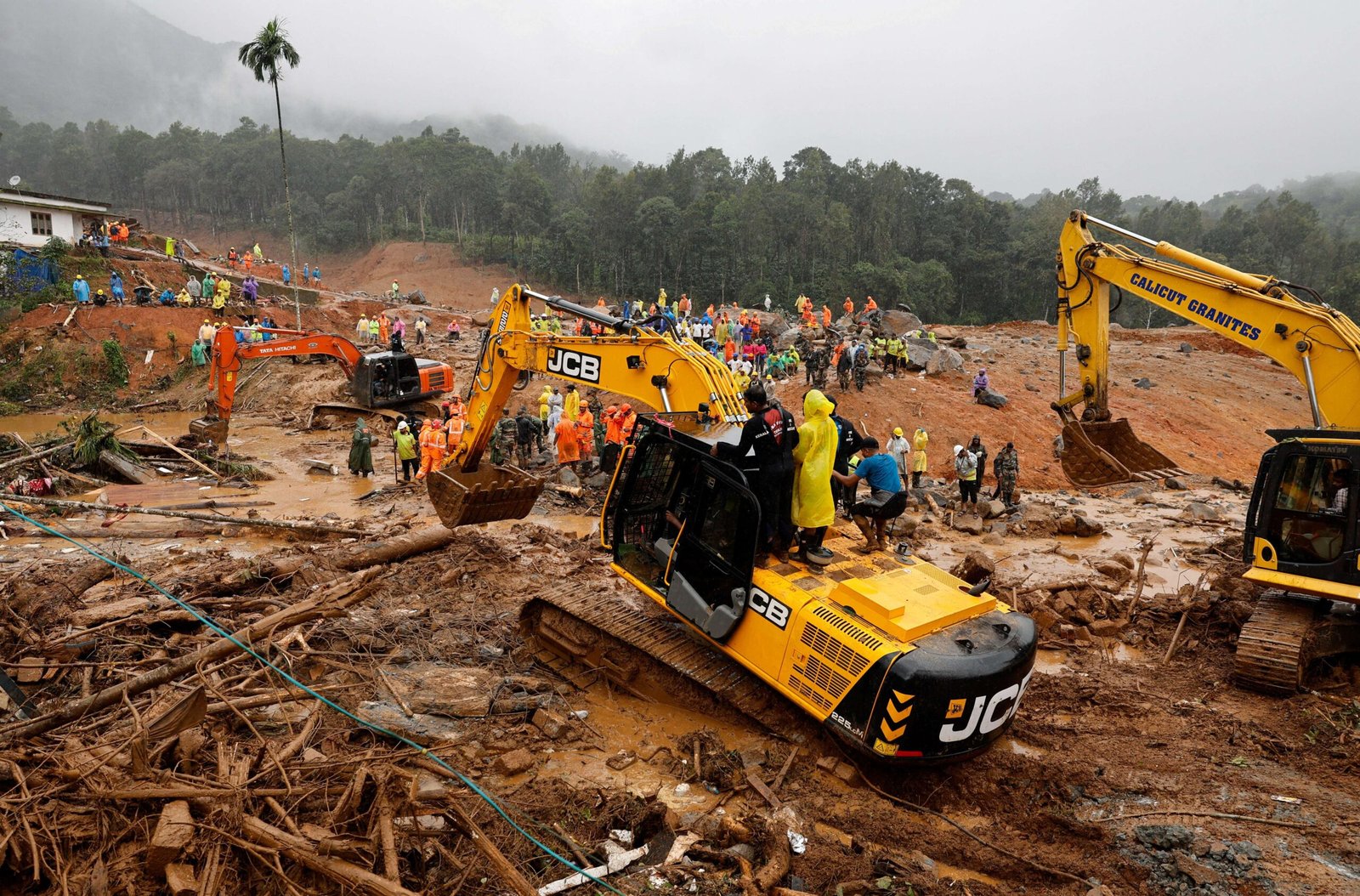
Wayanad Avalanches: Final Stages of Search Operations Focus on Remote Areas
The recent avalanches in Wayanad, Kerala, have left a significant impact on the region, with search and rescue teams now entering the final stages of their operations. This disaster has highlighted the immense challenges faced by those involved in recovery efforts, particularly as they shift their focus to the remote areas of Wayanad's rugged terrain. Here’s an in-depth look into the ongoing search operations, the affected areas, and the broader implications of this natural disaster.
1. Overview of the Wayanad Avalanches
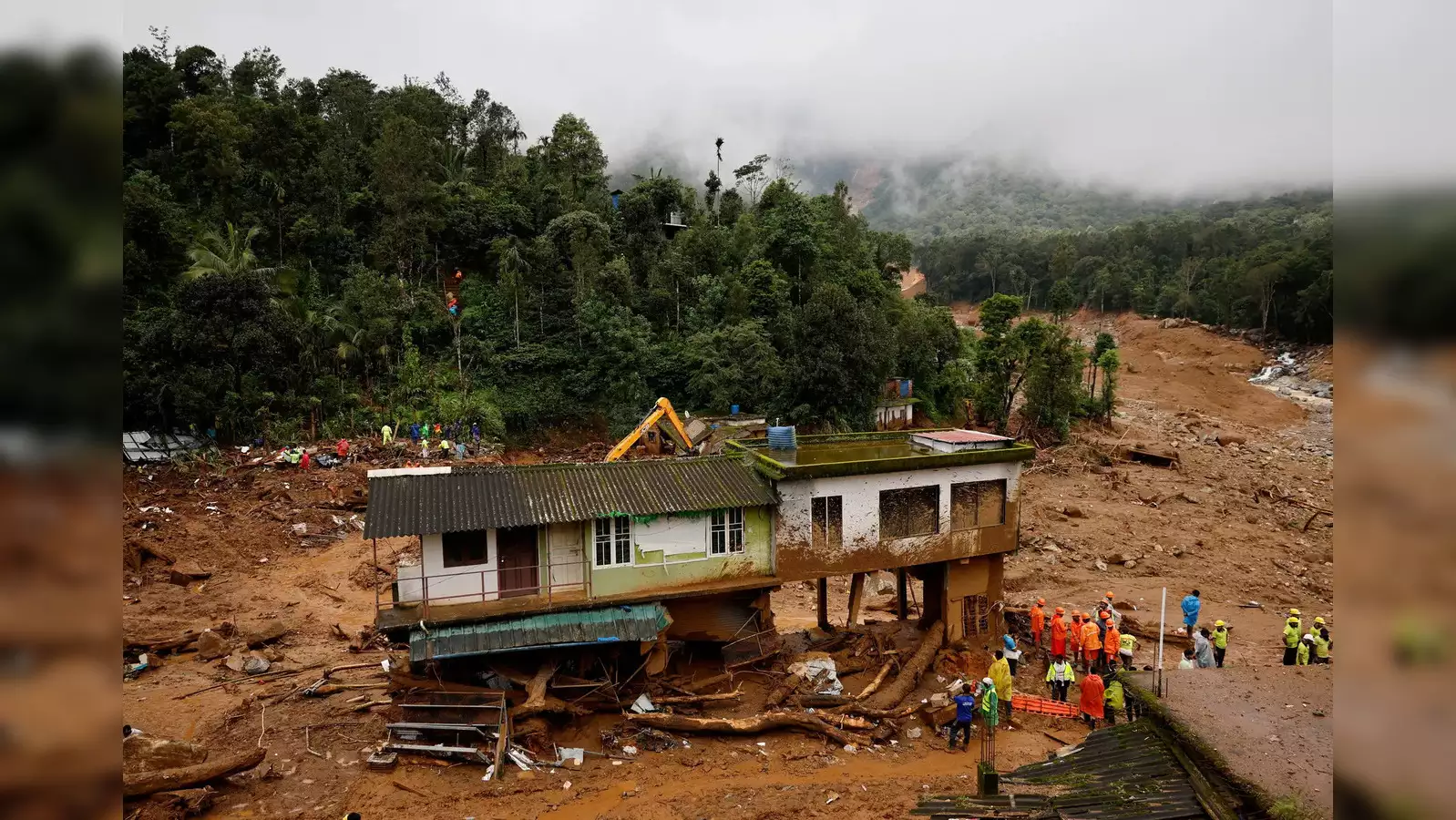

Wayanad, a picturesque district known for its lush greenery and beautiful landscapes, has been hit by a series of avalanches following unprecedented rainfall and subsequent landslides. These natural calamities have disrupted lives, destroyed infrastructure, and left several communities isolated. The avalanches in Wayanad are attributed to a combination of heavy rainfall and fragile geological conditions, which have exacerbated the scale and frequency of landslides in the region.
2. Search Operations: Phases and Progress
The search and rescue operations began as soon as reports of the avalanches emerged. Over the past few days, local authorities, along with the National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) and other emergency teams, have worked tirelessly to locate survivors, provide relief, and clear debris.
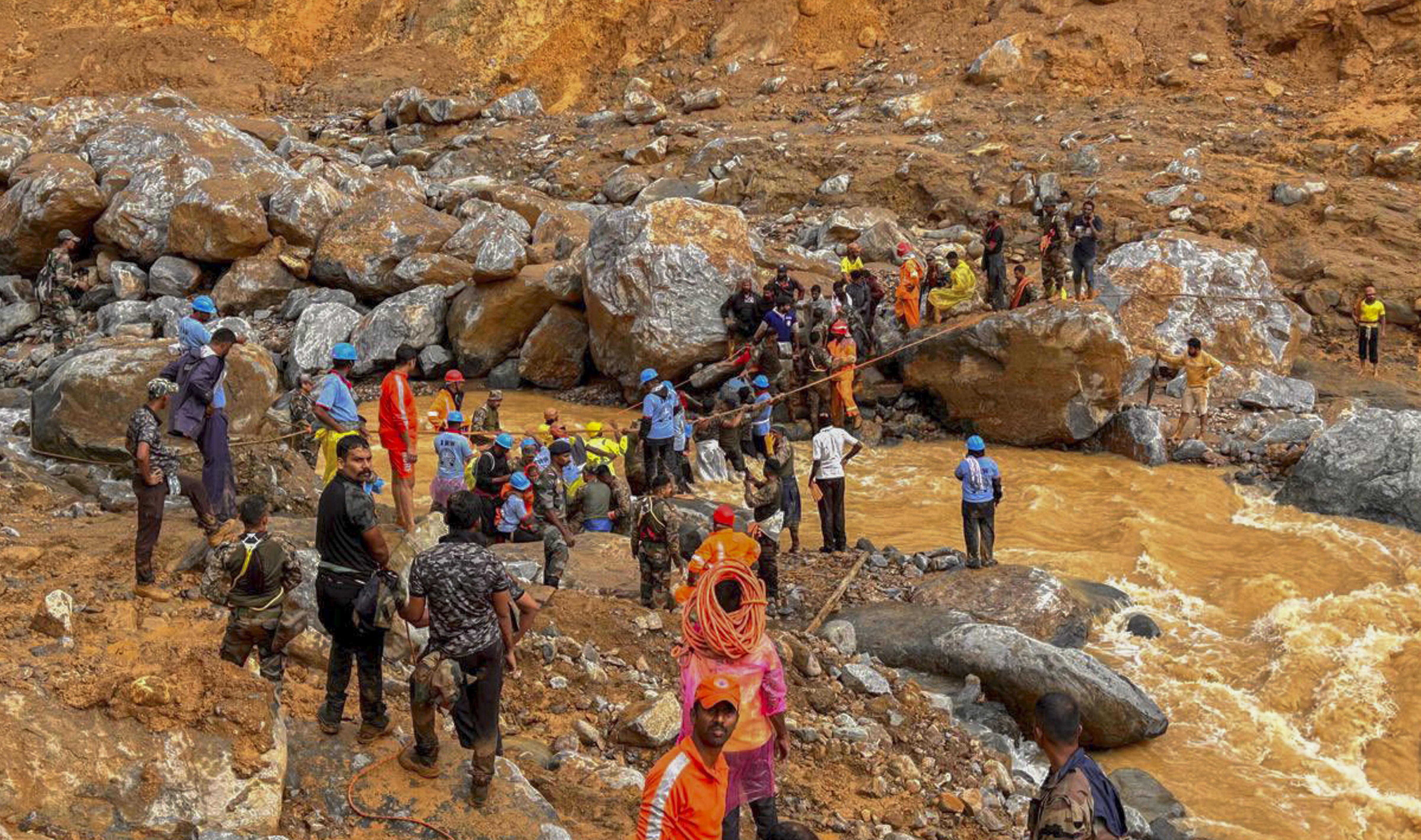

Initial Response: In the initial phase, teams focused on areas with high population density and locations where there were reports of missing persons. This phase involved extensive coordination between local authorities and national disaster response teams, with helicopters and ground vehicles deployed to transport supplies and personnel.
Mid-Phase Operations: The second phase expanded the scope of search operations to include areas that were partially accessible but potentially hazardous. Heavy machinery was brought in to clear major roadblocks and landslides that had rendered several areas inaccessible. Rescuers faced significant challenges due to the unstable terrain and adverse weather conditions.
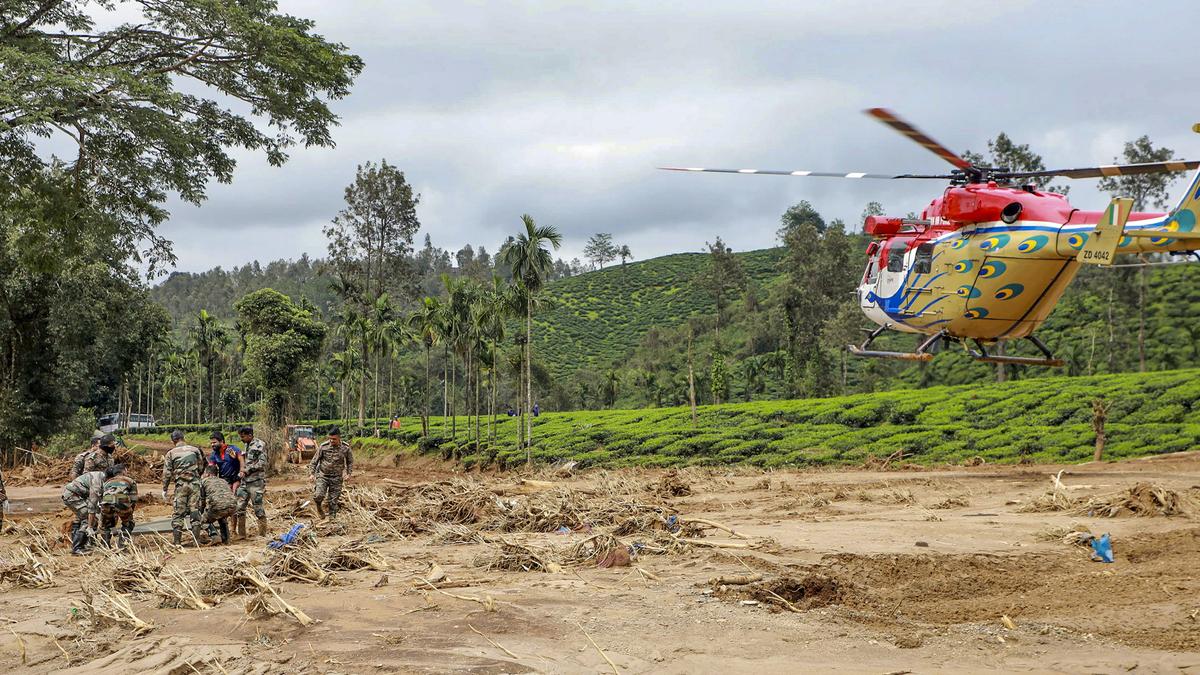

Final Phase: The final stage, which is currently underway, is focusing on the remote and difficult-to-access areas of Wayanad. These regions are characterized by dense forest cover and steep slopes, making it challenging for rescue teams to navigate. The objective of this phase is to ensure that no area is overlooked and that all affected communities are reached. Search dogs, drones, and other specialized equipment are being utilized to aid in this effort.
3. The Challenge of Reaching Remote Areas
The remote areas of Wayanad present unique challenges to rescue operations. Many of these locations are not easily accessible by road and require extensive trekking or helicopter support for personnel and supplies to reach them. The search teams are utilizing every available resource to navigate the rough terrain:

Topographical Challenges: The mountainous terrain of Wayanad, with its dense forests and steep inclines, has made access particularly difficult. In many cases, teams have to clear landslide debris manually to create paths for search and rescue personnel.
Weather Conditions: Intermittent rainfall continues to affect the region, hampering rescue efforts and increasing the risk of further landslides. Rescue teams are forced to constantly monitor weather updates and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Limited Communication Networks: The remoteness of these areas has also affected communication, making it harder for teams to coordinate with their base of operations. Portable satellite phones and walkie-talkies are being used to maintain contact, but connectivity issues have posed significant challenges in terms of efficient coordination.

4. Efforts to Support Affected Communities
Beyond rescue operations, relief teams are working to provide immediate support to affected communities. Many residents have lost their homes and livelihoods, while others are in urgent need of food, water, and medical assistance. Relief efforts have thus focused on delivering these essentials while also addressing the longer-term needs of the communities.
Setting Up Relief Camps: Temporary relief camps have been established in safer areas to shelter those displaced by the avalanches. These camps are providing food, water, and basic medical care to those affected. Additionally, efforts are being made to ensure that people receive psychological support to help them cope with the trauma of the disaster.

Medical Assistance: Medical teams are attending to those injured during the avalanches and those suffering from conditions exacerbated by the disaster, such as respiratory problems and stress-related ailments. Mobile medical units have been set up to reach areas where people cannot easily access health facilities.
5. Environmental Impact and Long-Term Recovery
The avalanches have left behind significant environmental damage, including deforestation, soil erosion, and disruption to local wildlife habitats. Experts warn that it may take years for the region to fully recover. Additionally, the disaster has underscored the vulnerability of Wayanad's ecosystem, which is sensitive to climate fluctuations and human activity.
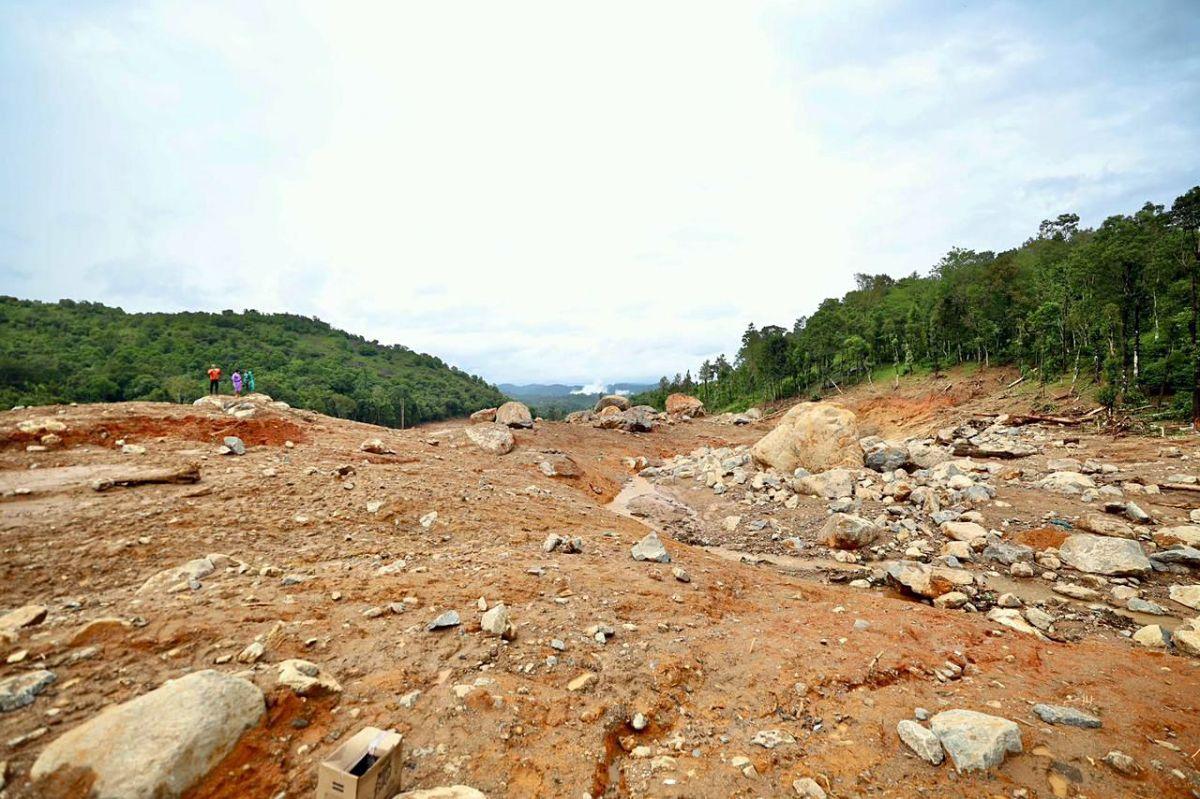

Soil Erosion and Deforestation: The heavy rains and subsequent landslides have led to significant soil erosion, particularly on steep slopes. This not only affects agriculture but also increases the risk of future landslides, as the destabilized soil is more prone to slipping.
Impact on Wildlife: Wayanad is home to a rich biodiversity, and the avalanches have disrupted the natural habitats of various species. Conservationists are concerned about the impact on local wildlife populations, especially in areas where trees and vegetation have been destroyed.
6. Lessons Learned and Future Preparedness
The Wayanad avalanches have highlighted the importance of disaster preparedness and the need for effective early warning systems in vulnerable regions. Authorities are likely to take several lessons from this disaster to improve response strategies for the future.
Conclusion
The Wayanad avalanches have tested the resilience and resolve of the affected communities and rescue teams. As the search operations move into their final stages, the focus remains on reaching every remote area and ensuring that no one is left behind. The disaster underscores the importance of preparedness and adaptability in the face of increasingly unpredictable weather patterns and natural disasters. Moving forward, there is a critical need for continued support, not only for the immediate recovery but also for building long-term resilience in the region.