In 2025, the film industry stands at the precipice of a technological revolution, driven largely by the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) rendering. The cinematic experience—once reliant almost entirely on human labor for scripting, animation, editing, and special effects—is now undergoing a radical transformation as AI steps into creative, logistical, and production roles. What was once science fiction is now a daily reality on film sets and in post-production studios across the globe.
AI rendering, a technique that uses machine learning algorithms to generate and refine visual content, has matured significantly in the last few years. In 2025, its impact on filmmaking is multi-dimensional, affecting how stories are told, how films are made, and even how they are consumed. From pre-visualization to deepfake technology and real-time CGI, AI is not just enhancing production quality—it is redefining the creative process itself.
The Rise of AI Rendering Technology
At the heart of AI’s influence on cinema is its rendering capability. Traditional rendering, particularly in computer-generated imagery (CGI), has always been a time-consuming process. Creating lifelike scenes, characters, and environments could take hours or days per frame, depending on complexity. However, AI rendering drastically accelerates this process by leveraging neural networks trained on massive visual datasets to “predict” and generate high-quality frames in real-time or near real-time.
Companies like NVIDIA, Unreal Engine, and OpenAI have developed systems that allow filmmakers to render complex scenes with minimal hardware and in a fraction of the time. In 2025, virtual production powered by AI enables directors to visualize entire worlds on set via LED walls, combining practical and digital elements seamlessly. The days of actors performing against green screens with only their imagination to guide them are fading.
Real-Time CGI and Virtual Sets
The growth of virtual sets is among the most obvious consequences of AI rendering. Shows like The Mandalorian popularized the use of LED volume stages, but in 2025, AI makes these sets even more dynamic. Filmmakers can alter settings, weather, or even camera angles in the middle of a shot without having to re-render thanks to real-time modifications and clever lighting algorithms.
AI-assisted virtual sets reduce both the cost and carbon footprint of location shooting. A cityscape in Tokyo, a desert in Namibia, or an underwater trench can be generated and modified instantly on a soundstage. This democratizes access to high-quality production tools, allowing indie filmmakers to achieve blockbuster visuals at a fraction of the budget.
AI-Driven Character Creation and Performance
Another frontier in AI rendering is the creation and manipulation of characters. In 2025, AI-generated avatars can be made photorealistic, with facial expressions and movements modeled after real human behavior. Actors no longer need to be physically present; they can license their likeness and have their “digital twin” perform in films. This is particularly useful for aging or deceased actors, raising both ethical and legal questions but also opening new creative doors.
Motion capture, once limited by expensive suits and specialized stages, is now achievable using standard cameras and AI tracking software. This democratization of mocap technology means more creators can bring richly expressive digital characters to life without a Hollywood budget.

AI in Scriptwriting and Storyboarding
Beyond visuals, AI is playing an increasing role in storytelling itself. AI-assisted screenwriting tools can analyze plot structure, dialogue pacing, and emotional arcs to help writers refine their scripts. Some studios now use generative AI to brainstorm story ideas, write dialogue, or create entire first drafts, which are then polished by human writers.
Storyboarding, a traditionally manual and iterative process, is now partly automated. With tools like Runway, Sora, and OpenAI’s image-generation models, filmmakers can generate highly detailed storyboards directly from text descriptions. This allows for quicker pre-production cycles and better alignment between creative vision and execution.
Deepfakes, Voice Cloning, and Ethical Concerns
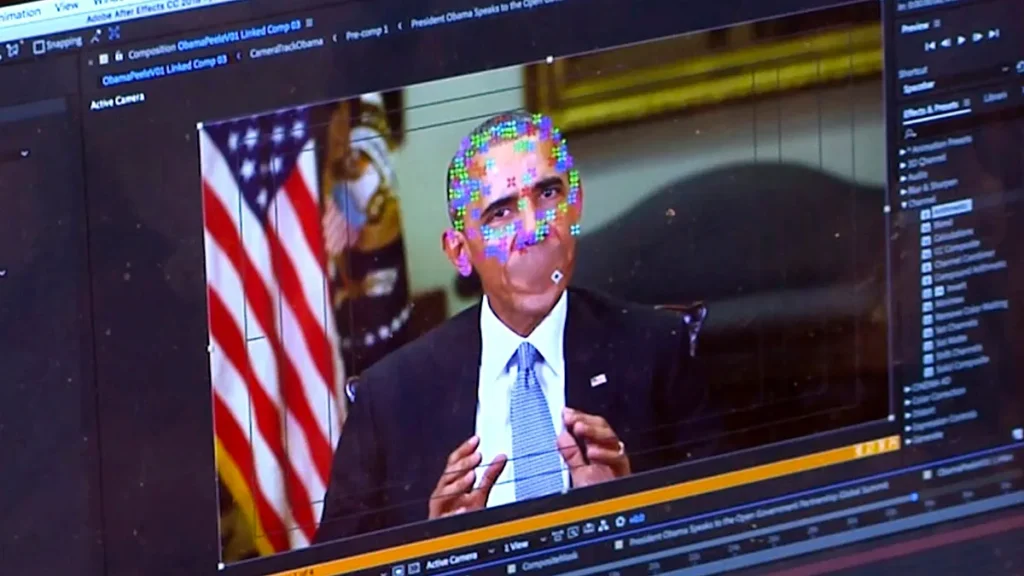
Deepfake technology is among the most contentious uses of AI in movies. By 2025, it will be almost impossible to tell artificial intelligence voices and faces apart from genuine ones. While this can be used to revive historical figures or age actors up or down convincingly, it also poses significant risks for misinformation, identity theft, and artistic authenticity.
Studios must navigate a complicated web of legal and ethical requirements. New industry guidelines now require explicit consent for AI-generated likenesses, and digital watermarking tools are being implemented to ensure transparency. Still, the debate continues: Does using AI replicas cheapen performance art, or does it offer new forms of creative expression?
Personalized and Interactive Films
AI is also reshaping how audiences experience film. With advanced rendering and real-time decision engines, personalized storytelling has become feasible. Platforms now offer interactive films that adapt in real time based on viewer choices, facial expressions, or even biometric feedback. AI customizes plot developments, character outcomes, and visual styles to cater to individual preferences.
Imagine watching a sci-fi thriller that changes its ending depending on your emotional engagement during key scenes, or an animated movie that mirrors your child’s voice in a character. These experiences are no longer theoretical—they are commercially viable in 2025.
AI and Post-Production Automation
AI is speeding up the post-production pipeline in the editing suite. With the use of director comments, tools may now automatically chop scenes, sync audio, color-correct, and even create substitute takes. Visual effects, once laborious and expensive, can now be implemented with a single prompt or reference image.
For example, if a director wants to see what a scene would look like at sunset instead of mid-day, AI can adjust lighting, shadows, and atmosphere across the entire sequence instantly. This level of flexibility is transforming the creative process, making iterative experimentation more accessible than ever.
New Roles, New Skills
New creative occupations are emerging as AI replaces some tasks that humans have historically performed. Prompt engineers, AI ethicists, digital likeness managers, and real-time scene supervisors are now part of production teams. The film industry in 2025 is not replacing human creativity—it’s augmenting it with powerful tools that expand what’s possible.
Education and training programs have adapted to this shift, teaching filmmakers how to collaborate with AI systems rather than compete with them. A new wave of hybrid creators is leading the charge—individuals equally fluent in storytelling and machine learning.
Conclusion: The Future of Filmmaking
The convergence of entertainment and AI rendering in 2025 represents not just a technological upgrade, but a reimagining of what cinema can be. Stories are being told faster, more vividly, and more inclusively. While challenges around authenticity, ethics, and labor displacement remain, the creative potential of AI is too significant to ignore.
As AI continues to evolve, the lines between filmmaker and machine, viewer and participant, real and virtual will continue to blur. In this new era, imagination is no longer constrained by the limits of time, budget, or physics—it’s only limited by the courage to innovate.
FAQs: AI Rendering and the Future of Filmmaking in 2025
1. What is AI rendering in filmmaking?
AI rendering is the process of using artificial intelligence algorithms—especially neural networks—to generate, enhance, or simulate visual elements in films. It drastically speeds up tasks like CGI, lighting, background generation, and scene composition, allowing filmmakers to create realistic visuals more efficiently.
2. How is AI different from traditional CGI rendering?
Traditional CGI rendering relies on manual modeling and computationally heavy processes, often requiring hours per frame. AI rendering uses trained models to “predict” visual outputs based on prior data, enabling faster and more intelligent image generation with less manual input.
3. Can AI really create entire characters or actors?
Yes, in 2025, AI can create hyper-realistic digital humans, including facial expressions, voices, and body movements. These can be based on real actors (with consent) or entirely synthetic personas, often referred to as “AI avatars” or “digital twins.”
4. What are AI-powered virtual sets, and how do they work?
Virtual sets use large LED walls and real-time rendering engines (like Unreal Engine) to create dynamic environments during filming. With AI, these sets can adapt lighting, textures, and scenes on the fly based on camera angles or director inputs—reducing the need for physical locations or post-production VFX.
5. Are AI-generated scripts or dialogue common now?
They’re becoming more common. While human writers are still central, AI tools assist with generating ideas, improving structure, suggesting dialogue, and analyzing emotional arcs. Some studios use AI for first drafts or to generate alternative scenes.
6. Is deepfake technology being used in Hollywood films?
Yes. Deepfake and voice cloning technologies are used to recreate actors (living or deceased), de-age them, or simulate stunts. However, strict ethical guidelines and actor consent are now required to prevent misuse.